Management of chemical substances
Management system for chemical substances
We recognize that identifying and managing the impacts chemical substances have on the environment and their safety is an important obligation of a paint manufacturer. Starting in fiscal 2010, we established a management system with expanded scope covering not only the environment, but also occupational safety and health and the safety of chemical products and paint products, and launched our Responsible Care activities.
Regulations on chemical substances span a multitude of laws both inside and outside of Japan. To remain informed about compliance with these regulations and revisions to laws in a reliable and accurate manner, we manage chemical substances appropriately through our Responsible Care activities.
Specifically, the Group Product Safety Committee, which is set up under the Responsible Care Committee, holds discussions with Group companies and prepares management standards to standardize the handling of chemical substances and prevent incorrect operation. We properly responded to domestic and international laws and regulations in fiscal 2020, including the submission of notifications in accordance with the revised Cabinet Order for the Designation of Poisonous and Deleterious Substances.
Approach to the management of chemical substances in products
Mitigating impacts on sustainability throughout the product life cycle is an important challenge. In particular, the management of risks related to hazardous chemical substances used in products from the raw materials and design stages is critical. In order to manage these risks, the Group has established rules on the prohibition or restricted use of substances based on the legislation of each region in an effort to mitigate risk.
As programs for chemical substance controls tailored to the actual situation of each region, the Group uses Green 30 in Japan, Chemicals of Concern in Australia, and Negative Substance List in China.
Voluntary initiatives for management of chemical substances
We have established our own voluntary green standards on chemical substances given the current situation of tightening controls around the world.
To enable chemical substance management following WSSD 2020 goal adopted at the Johanessburg Summit of 2002 (minimize chemical substance risk by 2020), up 2020 we had been using Green 20, our conventional standards, restricted to our partner companies in Japan. However, the globalization of our business has progressed rapidly and the importance of compliance with laws and regulations pertaining to chemical substances has increased further.
Given this background, voluntary standards for the management of chemical substances that can be applied broadly to all of our Group companies around the world were required to contribute to the promotion of ESG-driven management and Groupwide compliance.
Therefore, in fiscal 2021 we established Green 30, a voluntary standard for the sustainable development of the Group and society in general expanding the previous Green 20 standard used to implement our management system for chemical substances in order to minimize impacts on the environment caused by these substances to cover the entire Nippon Paint Group.
Under Green 30, we manage hazardous chemical substances according to ranks following the legislation of each country from their point of entry in the adoption stage so as to minimize risks. Rank A prohibits the use of prohibited substances under law and Rank B prohibits the new adoption of regulated substances per REACH in applicable countries and applications. In turn, these ranks are being used to phase out the use of these substances.
At the same time, we are exploring options for alternatives to replace chemical substances that pose a high risk.
For the interim, these standards will apply to our partner companies in Japan. The rollout of these standards for overseas partner companies will be determined at a later date.
Currently, we do not use lead compounds nor are they contained in our products. We have continued working, through our membership in the Japan Paint Manufacturers Association (JPMA), to reduce lead usage following the JPMA Board Resolution Regarding Lead Risk Reduction of Paints, and in 2019 we completely eliminated our use of lead compounds.
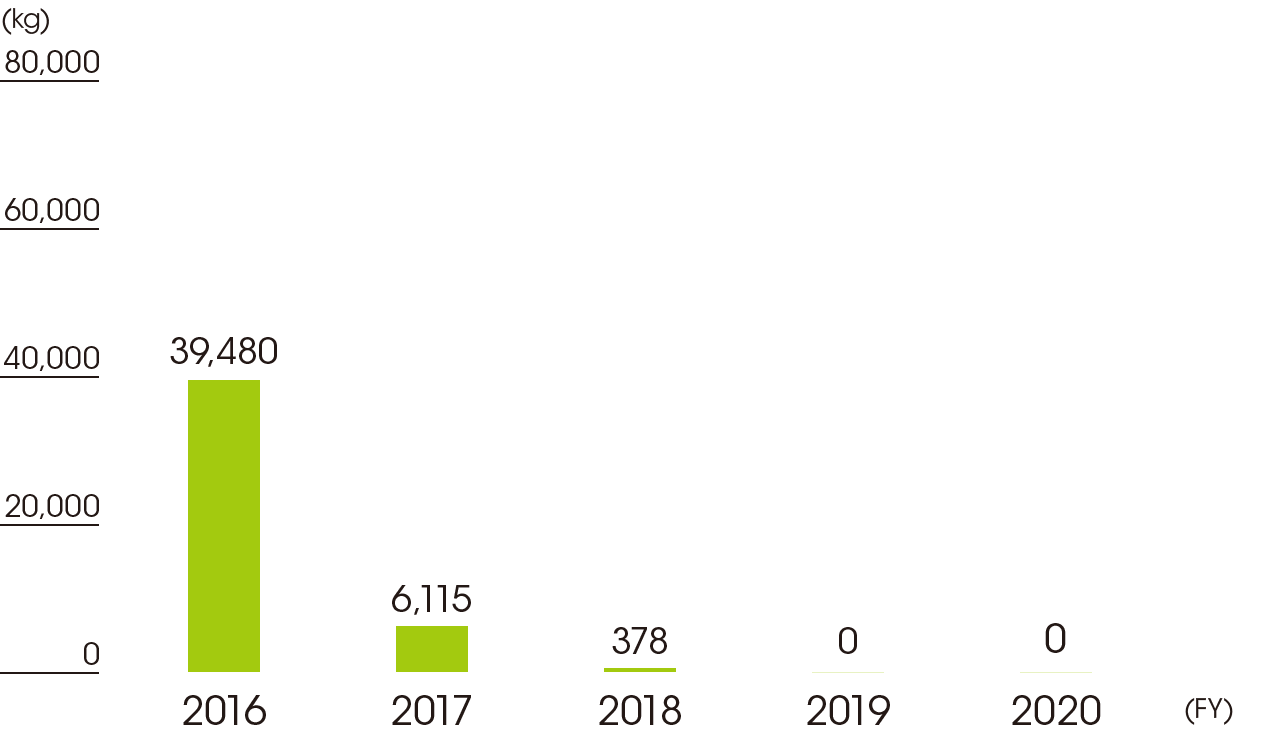
Responsible Care targets and results for chemical substances
| Priority themes | Targets for 2020 | Results in 2020 | Evaluation of 2020* | Targets for 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemicals and environmental safety | Initiatives on product launch and marketing to reduce environmental impacts
|
|
+++ |
ESG/SDGs-driven product launch and marketing initiatives
|
| Strengthen internal control | Management system for chemical substances
|
Found non-compliance (labelling, letter of transfer) at some OEMs according to the Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law, but confirmed completion of corrective measures. Established a system not only for our own products but also to maintain legal compliance for OEM products. | +++ | Follow-up on targets for 2020 |
* Evaluation standard: Domestic average achievement rate of +++: at least 80% or above, ++: at least 50%, +: less than 50%
Bold text for 2021 reflects changes from 2020
Information provision on chemical substance content
Paint contains various chemical substances originating from their raw materials, some of which can be harmful to the human body or the environment. We provide safety information on all products for countries that have adopted the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS) by using SDS (safety data sheet) and labels in accordance with GHS classification.
Chemical substance management at our factories
Measures to prevent the leakage and spillage of hazardous materials
We have implemented measures to prevent leaks and spills of hazardous materials, obtained materials for response to leaks and also provided training for the prevention of leakage and spillage of hazardous materials in an annual emergency drill organized in each area.
For example, this drill uses a scenario where products have leaked onto a surface road after an accident involving the truck transporting them. We then provide training for notifying related parties of the accident, preventing the spread of the leakage and recovering the products in order to develop the ability to respond quickly to emergencies.
In fiscal 2020, while the number of leakages during transportation decreased, there were two accidents involving leaks outside of the premises. The amounts were very small in both cases, and prompt response prevented impacts to water and soil.
However, we consider that the prevention and mitigation of leakages is a key issue to address. Therefore, we are enhancing measures such as adding transportation items to the RC target guidelines.
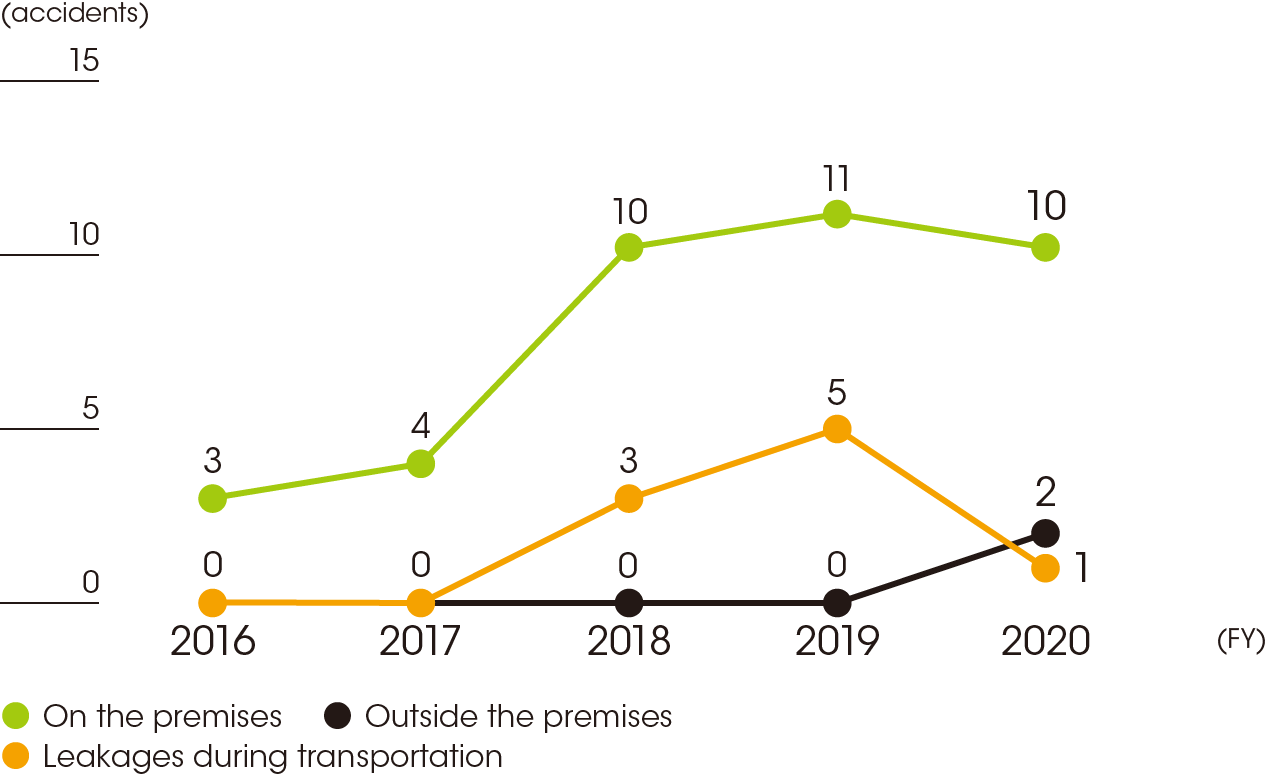
Reporting boundary:
FY2016 to FY2018: Nippon Paint Automotive Coatings (NPAC), Nippon Paint Industrial Coatings (NPIU), Nippon Paint (NPTU), Nippon Paint Surf Chemicals (NPSU), Nippon Paint Marine Coatings (NPMC) (April–December for FY2016)
FY2019 to FY2020: NPAC, NPIU, NPTU, NPSU, NPMC, AS Paint (ASP), AS Resin (ASR), and Nippon Paint Anti-Corrosive Coatings (NAC)
Chemical substances impact assessment / risk assessment
Following the revision of the Industrial Safety and Health Act, risk assessment on the hazard of chemical substances has become a requirement (674 substances; as of October 2021).
While the Group has always conducted risk assessment related to work safety, since the legal requirement came into effect, the Group is taking renewed measures to evaluate each chemical substance with potential risks or health hazard to workers for their risk and harmful effects. We are also implementing appropriate and effective risk reduction and response measures at each location based on the assessment results.
For details on overall risk assessment and targets, please see here.
